This library contains a set of reusable classes useful in ASP.NET Core for working with the Microsoft identity platform (formerly Azure AD v2.0 endpoint):
- Web applications that sign in users and, optionally, call web APIs
- Protected web APIs that optionally call downstream web APIs
In the library, web apps and protected web APIs are collectively referred to as web resources.
If you've been using Microsoft.Identity.Web in your projects, take note of these breaking changes introduced on the specified date.
- 02/18/2020
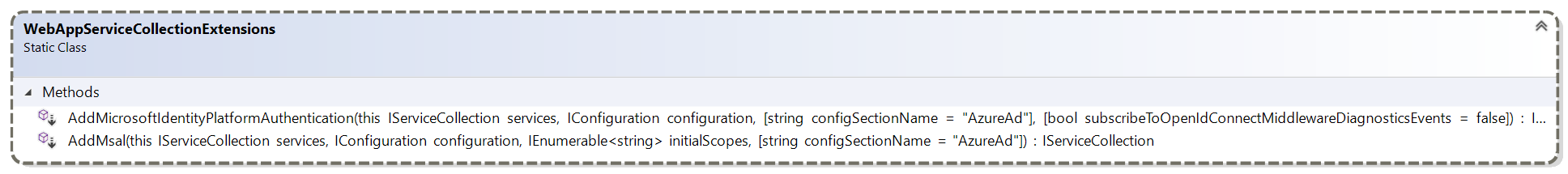
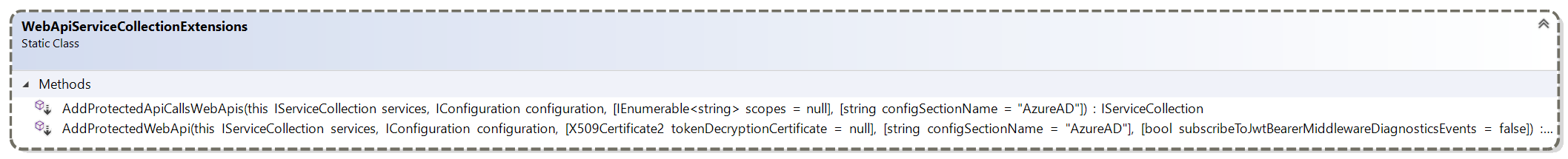
- Several APIs were renamed for consistency:
.AddMicrosoftIdentityPlatformAuthentication=>AddSignIn.AddMsal=>.AddWebAppCallsProtectedWebApi.AddProtectedWebApiCallsWebAPis=>AddProtectedWebApiCallsProtectedWebAPi
- Obsolete attributes were added to make it easier to migrate.
- Several APIs were renamed for consistency:
Currently, ASP.NET Core web app templates (dot net new mvc -auth) create web apps that sign in users with the Azure AD v1.0 endpoint, allowing users to sign in with their organizational accounts (also called Work or school accounts).
This library adds ServiceCollection extension methods for use in the ASP.NET Core web app Startup.cs file. These extension methods enable the web app to sign in users with the Microsoft identity platform and, optionally, enable the web app to call APIs on behalf of the signed-in user.
To enable users to sign in with the Microsoft identity platform, replace this code in your web application's Startup.cs file:
using Microsoft.Identity.Web;
public class Startup
{
...
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
...
services.AddAuthentication(AzureADDefaults.AuthenticationScheme)
.AddAzureAD(options => Configuration.Bind("AzureAd", options));
...
}
...
}...with this code:
using Microsoft.Identity.Web;
public class Startup
{
...
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
...
services.AddAuthentication(OpenIdConnectDefaults.AuthenticationScheme)
.AddSignIn("AzureAd", Configuration, options => Configuration.Bind("AzureAd", options));
...
}
...
}This method adds authentication with the Microsoft identity platform. This includes validating the token in all scenarios (single- and multi-tenant applications) in the Azure public and national clouds.
See also:
- ASP.NET Core Web app incremental tutorial chapter 1.1, Sign in users in your organization
- Web App that signs-in users scenario overview in the Microsoft identity platform documentation, and related articles
If you want your web app to call web APIs, add the .AddWebAppCallsProtectedWebApi() line, and then choose a token cache implementation, for example .AddInMemoryTokenCaches():
using Microsoft.Identity.Web;
public class Startup
{
const string scopesToRequest = "user.read";
...
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
...
services.AddSignIn(Configuration)
.AddWebAppCallsProtectedWebApi(new string[] { scopesToRequest })
.AddInMemoryTokenCaches();
...
}
...
}By default, AddSignIn gets the configuration from the "AzureAD" section of the configuration files. It has
several parameters you can change.
The proposed token cache serialization is in memory. You can also use the session cache, or various distributed caches.
For your web app to call web APIs on behalf of the signed-in user, add a parameter of type ITokenAcquisition to the constructor of your controller (the ITokenAcquisition service will be injected by dependency injection by ASP.NET Core).
using Microsoft.Identity.Web;
[Authorize]
public class HomeController : Controller
{
readonly ITokenAcquisition tokenAcquisition;
public HomeController(ITokenAcquisition tokenAcquisition)
{
this.tokenAcquisition = tokenAcquisition;
}
...Then, in your controller actions, call ITokenAcquisition.GetAccessTokenForUserAsync, passing the scopes for which to request a token. The other methods of ITokenAcquisition are used from the AddWebAppCallsProtectedWebApi() method and similar methods for web APIs (see below).
[Authorize]
public class HomeController : Controller
{
readonly ITokenAcquisition tokenAcquisition;
...
[AuthorizeForScopes(Scopes = new[] { "user.read" })]
public async Task<IActionResult> Action()
{
string[] scopes = new []{"user.read"};
string token = await tokenAcquisition.GetAccessTokenForUserAsync(scopes);
...
// call the downstream API with the bearer token in the Authorize header
}The controller action is decorated with the AuthorizeForScopesAttribute which enables it to process the MsalUiRequiredException that could be thrown by the service implementing ITokenAcquisition.GetAccessTokenOnBehalfOfUserAsync. The web app can then interact with the user and ask them to consent to the scopes, or re-sign in if needed.
You can learn how the library is used in the following samples:
- ASP.NET Core Web app incremental tutorial chapter 2.1, call Microsoft Graph on behalf of a signed in user
- ASP.NET Core Web app incremental tutorial chapter 2.2, call Microsoft Graph on behalf of a signed in user with a SQL token cache
- Web app that calls web apis scenario overview in the Microsoft identity platform documentation, and related articles
The Microsoft.Identity.Web library also enables web APIs to work with the Microsoft identity platform, enabling them to process access tokens for both work and school and Microsoft personal accounts.
To enable the web API to accept tokens emitted by the Microsoft identity platform, replace this code in your web API's Startup.cs file:
using Microsoft.Identity.Web;
public class Startup
{
...
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
...
services.AddAuthentication(AzureADDefaults.AuthenticationScheme)
.AddAzureAdBearer(options => Configuration.Bind("AzureAd", options));
...
}
...
}...with this code:
using Microsoft.Identity.Web;
public class Startup
{
...
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
...
services.AddProtectedWebApi(Configuration);
...
}
...
}This method enables your web API to be protected using the Microsoft identity platform. This includes validating the token in all scenarios (single- and multi-tenant applications) in the Azure public and national clouds.
See also:
- ASP.NET Core Web API incremental tutorial chapter 1.1, Protect the web API
- Protected web API scenario overview in the Microsoft identity platform documentation, and related articles
If you want your web API to call downstream web APIs, add the .AddProtectedWebApiCallsProtectedWebApi() line, and then choose a token cache implementation, for example .AddInMemoryTokenCaches():
using Microsoft.Identity.Web;
public class Startup
{
...
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
...
services.AddProtectedWebApi(Configuration)
.AddProtectedWebApiCallsProtectedWebApi()
.AddInMemoryTokenCaches();
...
}
...
}As with web apps, you can choose various token cache implementations.
If you're certain that your web API will need some specific scopes, you can optionally pass them as arguments to AddProtectedWebApiCallsProtectedWebApi.
To enable your web API to call downstream APIs:
-
Add (as in web apps) a parameter of type
ITokenAcquisitionto the constructor of your controller. TheITokenAcquisitionservice will be injected by dependency injection by ASP.NET Core. -
In your controller actions, verify that the token contains the scopes expected by the action. To do so, call the
VerifyUserHasAnyAcceptedScopeextension method on theHttpContext.
-
In your controller actions, call
ITokenAcquisition.GetAccessTokenForUserAsync, passing the scopes for which to request a token.
The following code snippet shows how to combine these steps:
[Authorize]
public class HomeController : Controller
{
readonly ITokenAcquisition tokenAcquisition;
static string[] scopeRequiredByAPI = new string[] { "access_as_user" };
...
public async Task<IActionResult> Action()
{
HttpContext.VerifyUserHasAnyAcceptedScope(scopeRequiredByAPI);
string[] scopes = new []{"user.read"};
try
{
string accessToken = await _tokenAcquisition.GetAccessTokenOnBehalfOfUser(scopes);
// call the downstream API with the bearer token in the Authorize header
}
catch (MsalUiRequiredException ex)
{
_tokenAcquisition.ReplyForbiddenWithWwwAuthenticateHeader(HttpContext, scopes, ex);
}
...
}When your web API tries to get a token for the downstream API, the token acquisition service may throw a MsalUiRequiredException. The MsalUiRequiredException indicates that the user on the client calling the web API needs to perform additional actions, for example, multi-factor authentication.
Given that the web API isn't capable of performing such interaction itself, the exception needs to be passed to the client. To propagate the exception back to the client, catch the exception and call the ITokenAcquisition.ReplyForbiddenWithWwwAuthenticateHeader method.
For web apps that call web APIs and web APIs that call downstream APIs, the code snippets above show the use of the In Memory token cache serialization. The library provides several alternate token cache serialization methods:
| Extension Method | Microsoft.Identity.Web sub namespace | Description |
|---|---|---|
AddInMemoryTokenCaches |
TokenCacheProviders.InMemory |
In memory token cache serialization. This implementation is great in samples. It's also good in production applications provided you don't mind if the token cache is lost when the web app is restarted. AddInMemoryTokenCaches takes an optional parameter of type MsalMemoryTokenCacheOptions that enables you to specify the duration after which the cache entry will expire unless it's used. |
AddSessionTokenCaches |
TokenCacheProviders.Session |
The token cache is bound to the user session. This option isn't ideal if the ID token is too large because it contains too many claims as the cookie would be too large. |
AddDistributedTokenCaches |
TokenCacheProviders.Distributed |
The token cache is an adapter against the ASP.NET Core IDistributedCache implementation, therefore enabling you to choose between a distributed memory cache, a Redis cache, or a SQL Server cache. For details about the IDistributedCache` implementations, see https://docs.microsoft.com/aspnet/core/performance/caching/distributed?view=aspnetcore-2.2#distributed-memory-cache. |
Examples of possible distributed cache:
// or use a distributed Token Cache by adding
services.AddSignIn(Configuration)
.AddWebAppCallsProtectedWebApi(new string[] { scopesToRequest })
.AddDistributedTokenCaches();
// and then choose your implementation
// For instance the distributed in memory cache (not cleared when you stop the app)
services.AddDistributedMemoryCache()
// Or a Redis cache
services.AddStackExchangeRedisCache(options =>
{
options.Configuration = "localhost";
options.InstanceName = "SampleInstance";
});
// Or even a SQL Server token cache
services.AddDistributedSqlServerCache(options =>
{
options.ConnectionString = _config["DistCache_ConnectionString"];
options.SchemaName = "dbo";
options.TableName = "TestCache";
});The library contains additional classes that you might find useful.
In web apps that sign in users, ASP.NET Core transforms the claims in the IDToken to a ClaimsPrincipal instance, held by the HttpContext.User property. In the same way, in protected web APIs, the claims from the JWT bearer token used to call the API are available in HttpContext.User.
The library provides extension methods to retrieve some of the relevant information about the user in the ClaimsPrincipalExtensions class.
If you want to implement your own token cache serialization, you might want to use this class, for instance to get the key of the token cache to serialize (typically GetMsalAccountId()).
In the other direction, ClaimsPrincipalFactory instantiates a ClaimsPrincipal from an account objectId and tenantId. These methods can be useful when the web app or the web API subscribes to another service on behalf of the user, and then is called back by a notification where the users are identified by only their tenant ID and object ID. This is the case, for instance, for Microsoft Graph Web Hooks notifications.
Finally, you can create a ClaimsPrincipal from an instance of MSAL.NET IAccount, using the ToClaimsPrincipal method in AccountExtensions.
To troubleshoot your web app, you can set the subscribeToOpenIdConnectMiddlewareDiagnosticsEvents optional boolean to true when you call AddSignIn. This displays in the output window the progression of the OpenID connect message through the OpenID Connect middleware (from the reception of the message from Azure Active directory to the availability of the user identity in HttpContext.User).
To troubleshoot your web API, you can set the subscribeToJwtBearerMiddlewareDiagnosticsEvents optional boolean to true when you call AddProtectedWebApi. Enabling these diagnostics displays in the output window the progression of the OAuth 2.0 message through the JWTBearer middleware (from the reception of the message from Azure Active directory to the availability of the user identity in HttpContext.User).
In both cases, you can set a breakpoint in the methods of the OpenIdConnectMiddlewareDiagnostics and JwtBearerMiddlewareDiagnostics classes respectively to observe values in the debugger.
If you want to customize the OpenIdConnectOption or JwtBearerOption but still want to benefit from the implementation provided by Microsoft.Identity.Web, you can do so in your Startup.cs file:
Let's take, for example, the AddProtectedWebApi method. In it, you'll see this event set up:
options.Events.OnTokenValidated = async context =>
{
// This check is required to ensure that the Web API only accepts tokens from tenants where it has been consented and provisioned.
if (!context.Principal.Claims.Any(x => x.Type == ClaimConstants.Scope)
&& !context.Principal.Claims.Any(y => y.Type == ClaimConstants.Scp)
&& !context.Principal.Claims.Any(y => y.Type == ClaimConstants.Roles))
{
throw new UnauthorizedAccessException("Neither scope or roles claim was found in the bearer token.");
}
await Task.FromResult(0);
};Say you want to augment the current ClaimsPrincipal by adding claims to it, and you have to do it on OnTokenValidated . However, you don't want to lose the UnauthorizedAccessException check existing in the event. To do so, in your Startup.cs, you'd have:
services.AddProtectedWebApi(Configuration);
services.Configure<JwtBearerOptions>(AzureADDefaults.JwtBearerAuthenticationScheme, options =>
{
var existingOnTokenValidatedHandler = options.Events.OnTokenValidated ;
options.Events.OnTokenValidated = async context =>
{
await existingOnTokenValidatedHandler(context);
// your code to add extra claims that will be executed after the current event implementation.
}
}You can learn more about the tokens by looking at the following articles in MSAL.NET's conceptual documentation:
- The Authorization code flow, used to get a token and cache it for later use after the user signs in with Open ID Connect. See TokenAcquisition L 107 for details of this code.
- AcquireTokenSilent, used by the controller to get an access token for the downstream API. See TokenAcquisition L 168 for details of this code.
- Token cache serialization
Token validation is performed by the classes in the Identity Model Extensions for .NET library. Learn about customizing token validation by reading:
- Validating Tokens in that library's conceptual documentation
- TokenValidationParameters's reference documentation