UniGame Reactive Node System for Unity
Add to your project manifiest by path [%UnityProject%]/Packages/manifiest.json these lines:
{
"scopedRegistries": [
{
"name": "Unity",
"url": "https://package.unity.com",
"scopes": [
"com.unity"
]
},
{
"name": "UniGame",
"url": "http://packages.unigame.pro:4873/",
"scopes": [
"com.unigame"
]
}
],
}Open window Package Manager in Unity and install UniGame Nodes System Package
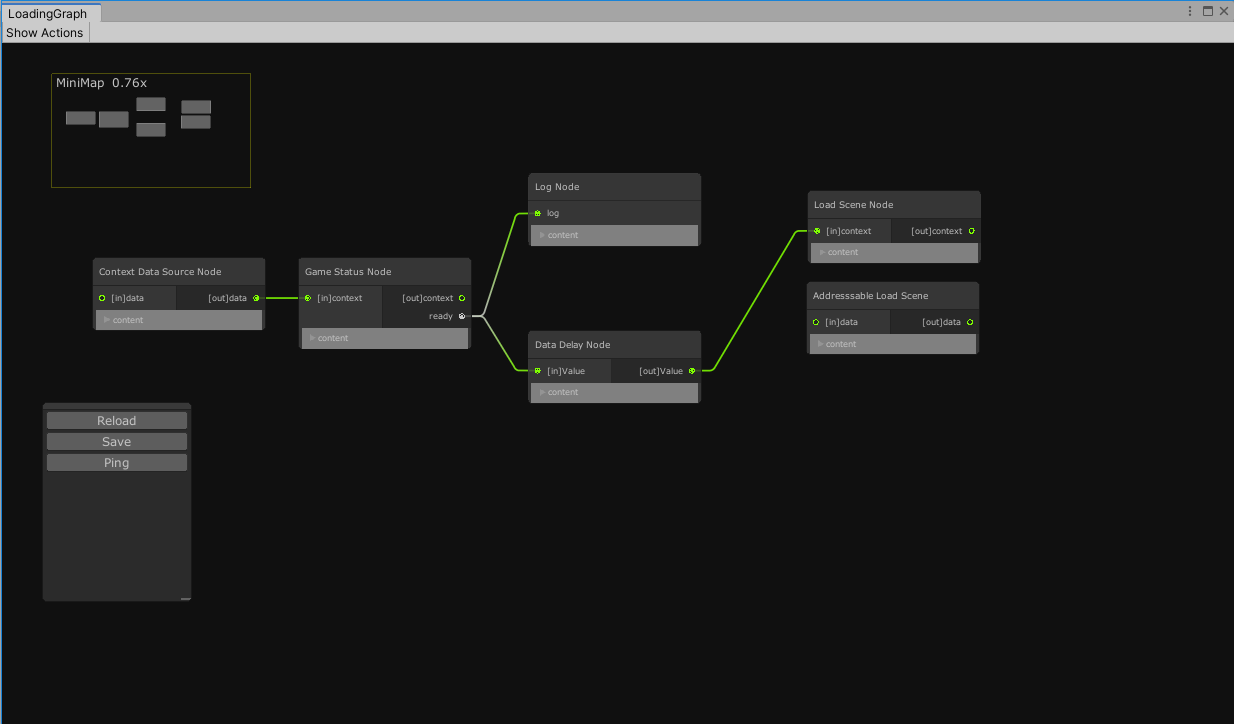
After that you already can view Graph Editor by clicking "Show Graph" button on prefab
Each graph - regular Unity Prefab Object.
Yout can create new Node woth two ways:
- As Unity Component Asset. Create new class file with inheritance from UniNode base class. When you create you node, there is several suitable methods for override
public class DemoComponentNode : UniNode
{
}- Serializable Class Object. As before create you custom class, but based on SNode class (Serializable Node). Don't forget mark your class with [Serializable] attribute
[Serializable]
public class DemoComponentNode : SNode
{
}For any custom node your can define menu name:
[CreateNodeMenu("Examples/DemoComponent","DemoComponent")]
public class DemoComponentNode : UniNode
{
}- Initialization. Allow you to initialize your node data, one time per whole graph lifetime
protected virtual void OnInitialize(){}- Execution. Custom logic for handle each 'Graph.Execute()' execution call
protected virtual void OnExecute(){}- Commands. Allow you add your custom node commands for nodes and separate your execution into small reusable pieces
protected virtual void UpdateCommands(List<ILifeTimeCommand> nodeCommands){}After that your can define your own node ports
public class DemoComponentNode : UniNode
{
[Port(PortIO.Input)]
public object inPort;
[Port(PortIO.Output)]
public object outPort;
}Any defined port can be requested by it name
[Serializable]
public class DemoComponentNode : SNode
{
[Port(PortIO.Input)]
public object inPort;
protected override void OnExecute()
{
var port = GetPort(nameof(inPort));
}
}Type of port field that's defined with attributes uses as type filter. Except of System.Object type. Port with System.Object type interpret as port of any type.
[Port(PortIO.Input)]
public object anyTypePort;
[Port(PortIO.Input)]
public int intTypePort;
[Port(PortIO.Input)]
public ISomeApi someApiTypePort;Besides of attribute usage you can define new port with declaration from the code
[Serializable]
public class DemoComponentNode : SNode
{
protected override void UpdateCommands(List<ILifeTimeCommand> nodeCommands)
{
var newPort = this.UpdatePortValue("newPost1",PortIO.Output);
var newPort2 = AddPort("newPort2", Enumerable.Empty<Type>(), PortIO.Output);
}
}Receive port data
When you retrive runtime port handle, you can subscribe for it input data stream
[Serializable]
public class DemoComponentNode : SNode
{
[Port(PortIO.Input)]
public int intPort;
protected override void OnExecute()
{
var intPortHandle = GetPort(nameof(intPort));
var portValue = intPortHandle.Value;
portValue.Receive<int>().
Subscribe(x => Debug.Log($"RECEIVE INT VALUE {x}")).
AddTo(LifeTime);
}
}Receive() - Allow you to create strong typed data stream. With that you can handle any new incomming port data of that type.
see UniRx for more information about reactive streams (https://github.com/neuecc/UniRx)
Instead of call GetPort(nameof(intPort)) you can call GetPortValue(%PORT_NAME%) method
[Serializable]
public class DemoComponentNode : SNode
{
[Port(PortIO.Input)]
public int intPort;
protected override void OnExecute()
{
var portValue = GetPortValue(nameof(intPort));
portValue.Receive<int>().
Subscribe(x => Debug.Log($"RECEIVE INT VALUE {x}")).
AddTo(LifeTime);
}
}Publish port data
[Serializable]
public class DemoComponentNode : SNode
{
[Port(PortIO.Output)]
public int outPort1;
[Port(PortIO.Output)]
public int outPort2;
//inspector value
public int outputValue = 333;
protected override void OnExecute()
{
var outPortHandle = GetPort(nameof(outPort1));
var portValue1 = outPortHandle.Value;
var portValue2 = GetPortValue(nameof(outPort2))
portValue1.Publish<int>(outputValue);
portValue2.Publish(outputValue * outputValue);
}
}In some cases your want to establish connection between ports for transferring all data from one to another. To easily achieve this use following:
public class DemoNode : UniNode
{
[Port(PortIO.Input)]
public object input1;
[Port(PortIO.Input)]
public object input2;
[Port(PortIO.Output)]
public object output;
protected override void OnExecute()
{
var inputValue1 = GetPortValue(nameof(input1));
var inputValue2 = GetPortValue(nameof(input2));
var outputValue = GetPortValue(nameof(output));
//Bind Output Port With input data
//Now All Data from inputs will be transferred to output
inputValue1.Bind(outputValue).AddTo(LifeTime);
inputValue2.Bind(outputValue).AddTo(LifeTime);
}
}What is AsyncState? This is special type of node that allow you define custom async execution operations:
- Async Await execution syntax support
- Flow tree execution or state machine logic
- Custom execution contoller override
- Rollback logic support
- Data transfer between states
All AsyncState based on API
- Command execution interface
public interface IAsyncCommand<TValue,T>
{
UniTask<T> ExecuteAsync(TValue value);
}- Async end point interface:
public interface IAsyncEndPoint
{
UniTask ExitAsync();
}- Async Rollback interface
public interface IAsyncRollback<TSource>
{
UniTask Rollback(TSource source);
}- Async operation completion handler
public interface IAsyncCompletion<TResult,TData>
{
UniTask CompleteAsync(TResult value, TData data, ILifeTime lifeTime);
}All of theese API grouped into two base graph node:
- Regular serializable class node AsyncStateNode
[Serializable]
public abstract class AsyncStateNode : SNode- Component based node AsyncStateUniNode
public abstract class AsyncStateUniNode : UniNodeEach of these node allow you to override execution flow methods for custom behaviour logic
here is default implementation
#region custom execution handlers
/// <summary>
/// Regular Execution logic behaviour
/// </summary>
public virtual UniTask<AsyncStatus> ExecuteStateAsync(IContext value) => UniTask.FromResult(AsyncStatus.Succeeded);
/// <summary>
/// state completion handler
/// </summary>
public virtual UniTask CompleteAsync(AsyncStatus value, IContext data, ILifeTime lifeTime) => UniTask.FromResult(UniTask.CompletedTask);
/// <summary>
/// Exiting from state handler
/// </summary>
public virtual UniTask ExitAsync(IContext data) => UniTask.FromResult(UniTask.CompletedTask);
/// <summary>
/// Execution Failure result handler
/// </summary>
public virtual UniTask Rollback(IContext source) => UniTask.FromResult(UniTask.CompletedTask);
#endregionThis is status of async operation:
public enum AsyncStatus {
/// <summary>The operation has not yet completed.</summary>
Pending = 0,
/// <summary>The operation completed successfully.</summary>
Succeeded = 1,
/// <summary>The operation completed with an error.</summary>
Faulted = 2,
/// <summary>The operation completed due to cancellation.</summary>
Canceled = 3
}You may ask What about data transfering between AsyncStates?
So, you have several options here:
- Send data through Ports
public override async UniTask<AsyncStatus> ExecuteStateAsync(IContext value)
{
var stringPortValue = GetPortValue(nameof(stringInput));
var message = await stringPortValue.Receive<string>().First();
Debug.Log($"GOT MESSAGE : {message}");
return AsyncStatus.Succeeded;
}- Send or Receive data directly through shared states context
public override async UniTask<AsyncStatus> ExecuteStateAsync(IContext value)
{
await UniTask.Delay(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(2));
value.Publish($"DELAY FINISHED {nodeName}");
return AsyncStatus.Succeeded;
}public override async UniTask<AsyncStatus> ExecuteStateAsync(IContext value)
{
var message = await value.Receive<string>().First();
Debug.Log($"GOT MESSAGE : {message}");
return AsyncStatus.Succeeded;
}AsyncState execution controlling by IAsyncStateToken
public interface IAsyncStateToken :
ILifeTimeContext,
IDisposable
{
IContext Context { get; }
int Id { get; }
/// <summary>
/// Try to launch target state for this execution token
/// </summary>
UniTask<bool> TakeOwnership(IAsyncContextState state);
/// <summary>
/// stop all state "after"(exclude) target state
/// </summary>
UniTask<bool> StopAfter(IAsyncContextState state);
/// <summary>
/// stop all state "since"(include) target state
/// </summary>
UniTask<bool> StopSince(IAsyncContextState state);
}Out of the box exists two implementation:
- SingleAsyncStateToken - "state mechine" like execution behaviour. Each new token owner stop previous one when receive token premitions
- FlowAsyncStateToken - flow execition. Any new state added into end of execution queue. When one state execution stoped, all added later stprocesses stoped too
For each node you can define information with attribute: NodeInfo
[CreateNodeMenu("Debug/Log","Log")]
[NodeInfo("Logging Node","Profiling","Logging all data from input port")]
public class LogNode : UniNode All list of available node can be found with "Show Nodes" button
At Any moment of Graph execution you can check - What kind of data that port contains?
- Node Graph Processor https://github.com/alelievr/NodeGraphProcessor