Unified Queries defined a Domain-Specific Language (DSL) to describe a common schema of a query specification. It also provides the ability to compile/translate the given query specification into another representation, for example,
- SQL WHERE clauses for RDBMS
- Lambda Expressions used by Entity Framework or Object Query
Moreover, the Unified Queries framework is very flexible and open for extending. You can implement your own compilers by either implementing the IQuerySpecificationCompiler interface, or inheriting the QuerySpecificationCompiler<T> base class.
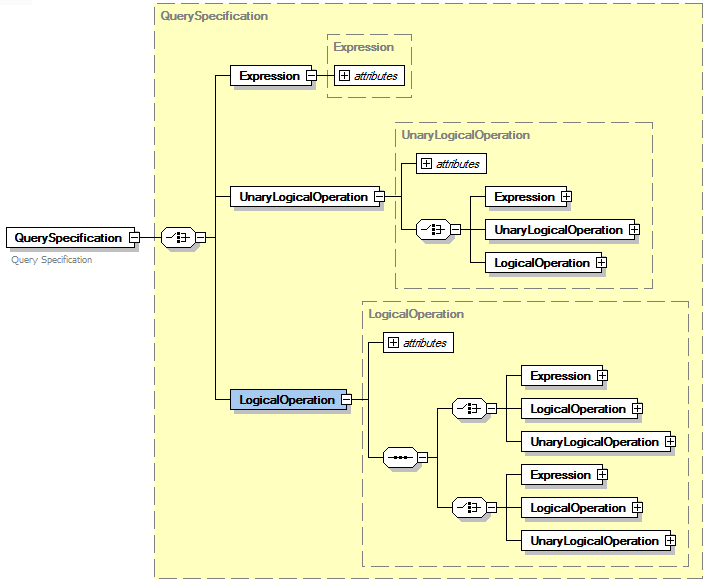
Unified Queries used the following XSD schema to describe the sematics of a query.
Suppose we have the following query specification defined in an XML file, say QuerySpecificationSample.xml, by executing this query, users would like to find out all the customers whose first name is starting with the string "Peter", and the last name of the customer doesn't contain the character "r", and the yearly income is greater than 30000.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<QuerySpecification>
<LogicalOperation Operator="And">
<Expression Name="FirstName" Type="String" Operator="StartsWith" Value="Peter"/>
<UnaryLogicalOperation Operator="Not">
<LogicalOperation Operator="Or">
<Expression Name="LastName" Type="String" Operator="Contains" Value="r"/>
<Expression Name="YearlyIncome" Type="Decimal" Operator="LessThanOrEqualTo" Value="30000"/>
</LogicalOperation>
</UnaryLogicalOperation>
</LogicalOperation>
</QuerySpecification>
Following C# code will generate a SQL WHERE clause statement:
static void Main(string[] args)
{
var querySpecification = QuerySpecification.LoadFromFile("QuerySpecificationSample.xml");
var compiler = new SqlWhereClauseCompiler();
Console.WriteLine(compiler.Compile(querySpecification));
}
The generated SQL WHERE clause is as follows:
((FirstName LIKE 'Peter%') AND (NOT ((LastName LIKE '%r%') OR (YearlyIncome <= 30000))))
Actually in most cases, developers working with ADO.NET always like to use the DbParameters, instead of putting the value directly in the generated SQL statement. Unified Queries also provides developers the ability of creating a SQL WHERE clause with a parameter list. Simply specify the useParameter parameter to true when constructing the SqlWhereClauseCompiler class:
var compiler = new SqlWhereClauseCompiler(true);
Finally you will get the following result:
((FirstName LIKE @fvP8gN) AND (NOT ((LastName LIKE @ESzoyd) OR (YearlyIncome <= @fG5Z7e))))
Note that this SQL WHERE clause is generated based on Microsoft SQL Server syntax. You can extend the SqlWhereClauseCompiler to fit other RDBMS needs.
Later, you can get the values for these generated parameters by using the ParameterValues property on the SqlWhereClauseCompiler.
Following C# code will generate a Lambda Expression based on the same query specification:
static void Main(string[] args)
{
var querySpecification = QuerySpecification.LoadFromFile("QuerySpecificationSample.xml");
var compiler = new LambdaExpressionCompiler<Customer>();
Console.WriteLine(compiler.Compile(querySpecification));
}
The output will be:
p => (p.FirstName.StartsWith("Peter") AndAlso Not((p.LastName.Contains("r") OrElse (p.YearlyIncome <= 30000))))
Suppose we have a list of Customers, following shows a full example of using the Lambda Expression to query a list of objects for the Customers with specific criteria.
private static Customer[] GetAllCustomers()
{
return new[]
{
new Customer { FirstName = "Sunny", LastName = "Chen", YearlyIncome = 10000 },
new Customer { FirstName = "PeterJam", LastName = "Yo", YearlyIncome = 10000 },
new Customer { FirstName = "PeterR", LastName = "Ko", YearlyIncome = 50000 },
new Customer { FirstName = "FPeter", LastName = "Law", YearlyIncome = 70000 },
new Customer { FirstName = "Jim", LastName = "Peter", YearlyIncome = 30000 }
};
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
var querySpecification = QuerySpecification.LoadFromFile("QuerySpecificationSample.xml");
var compiler = new LambdaExpressionCompiler<Customer>();
var customers = GetAllCustomers();
foreach (var customer in customers.Where(compiler.Compile(querySpecification).Compile()))
{
Console.WriteLine(
"FirstName: {0}, LastName: {1}, YearlyIncome: {2}",
customer.FirstName,
customer.LastName,
customer.YearlyIncome);
}
}