The Structure of Sequence Stack and Linked Stack
The Structure of Sequence Stack and Linked Stack
The Structure of String Class
Insert sort is a simple sorting algorithm. The principle is to scan the unsorted data from back to front in the sorted sequence, find the corresponding position and insert. In the process of backward scanning, the sorted elements need to be moved backward step by step repeatedly to provide insertion space for the latest elements.
Time Complexity:
* Average: O (n ^ 2)
* Best: O(n)
* Worst: O (n ^ 2)
Selection sort is a simple sorting algorithm. It works as follows: First, find the smallest (large) element in the unsorted sequence, store it at the beginning of the sorted sequence, then continue to find the smallest (large) element from the remaining unsorted elements, and then put it at the end of the sorted sequence. and so on until all the elements are sorted.
Time Complexity:
* O (n ^ 2)
QuickSort used a strategy called Divide & Conquer. The basic principle of Divide&Conquer is to decompose the problem into servial smaller sub-problems with similar structure to the original problem. Solve these subproblems recursively, and then combine the solutions of these subproblems into the solutions of the original problem.
Divide & Conquer can be used to divide quicksort into 3 steps:
- Select an Element as the "pivot" int the data set.
- All elements less than the "pivot" are moved to the left of the "pivot"; All elements larger than the "pivot" are moved to the right of the "pivot".
- For the left and right subsets of "pivot", repeat step 1 and step 2 until only one element is left in all subsets.
Time Complexity:
* Average: O (nlogn)
* Best: O (nlogn)
* Worst: O (n ^ 2)
Merge-Sort is an effective sorting algorithm established on merge operations. This algorithm is a typical application of Divide & Conquer. The Principle of the Merge-Sort is to merge the ordered subsequences to get a completely ordered sequence. Firstly, make each sub-sequence orderly, and then make the sub-sequence segments orderly
Time Complexity:
* Average: O (nlogn)
* Best: O (nlogn)
* Worst: O (nlogn)
Find the largest sub array in a array:
- Brute Force Method
- Divide & Conquer Method
Question: Design the encode and decode methods. There is no restriction on how your encode/decode algorithm should work. You just need to ensure that a string can be encoded to a a code and the code can be decoded to the original URL.
Question: Design a max stack that supports push, pop, peek, peekMax and popMax.
1. push(x) -- Push element x onto stack.
2. pop() -- Remove the element on top of the stack and return it.
3. peek() -- Get the element on the top.
4. peekMax() -- Retrieve the maximum element in the stack.
5. popMax() -- Retrieve the maximum element in the stack, and remove it. If you find more than one maximum elements, only remove the top-most one.
Question: International Morse Code defines a standard encoding where each letter is mapped to a series of dots and dashes, as follows: "a" maps to ".-", "b" maps to "-...", "c" maps to "-.-.", and so on.
For convenience, the full table for the 26 letters of the English alphabet is given below:
[".-","-...","-.-.","-..",".","..-.","--.","....","..",".---","-.-",".-..","--","-.","---", ".--.","--.-",".-.","...","-","..-","...-",".--","-..-","-.--","--.."]
Now, given a list of words, each word can be written as a concatenation of the Morse code of each letter. For example, "cba" can be written as "-.-..--...", (which is the concatenation "-.-." + "-..." + ".-"). We'll call such a concatenation, the transformation of a word. Return the number of different transformations among all words we have.
Example:
Input: words = ["gin", "zen", "gig", "msg"]
Output: 2
Explanation:
The transformation of each word is:
1. "gin" -> "--...-."
2. "zen" -> "--...-."
3. "gig" -> "--...--."
4. "msg" -> "--...--."
There are 2 different transformations, "--...-." and "--...--.".
Question: Every email consists of a local name and a domain name, separated by the @ sign. For example, in alice@leetcode.com, alice is the local name, and leetcode.com is the domain name. Besides lowercase letters, these emails may contain '.'s or '+'s.
If you add periods ('.') between some characters in the local name part of an email address, mail sent there will be forwarded to the same address without dots in the local name. For example, "alice.z@leetcode.com" and "alicez@leetcode.com" forward to the same email address. (Note that this rule does not apply for domain names.)
If you add a plus ('+') in the local name, everything after the first plus sign will be ignored. This allows certain emails to be filtered, for example m.y+name@email.com will be forwarded to my@email.com. (Again, this rule does not apply for domain names.) It is possible to use both of these rules at the same time.
Given a list of emails, we send one email to each address in the list. How many different addresses actually receive mails?
Example 1:
Input: ["test.email+alex@leetcode.com","test.e.mail+bob.cathy@leetcode.com","testemail+david@lee.tcode.com"]
Output: 2
Explanation: "testemail@leetcode.com" and "testemail@lee.tcode.com" actually receive mails
A Binary Tree is a finite set of n nodes, which can be an empty set (called an empty binary tree), or a root node and a binary tree of two disjoint nodes, called the left subtree of the root node and the right subtree respectively.
Binary tree traversal refers to starting from the root node, in some order to access all nodes in the binary tree, so that each node is accessed once. Include:
1. Preorder Traversal (前序遍历) ( node - left - right )
2. Inorder Traversal (中序遍历) ( left - node - right )
3. PostOrder Traversal (后序遍历) ( left - right - node )
4. LevelOrder Traversal(存序遍历) 从树的第一层开始,从上到下逐层遍历,在同一层中,从左到右对结点 逐个访问输出.
Binary sort tree, also known as binary search tree. It's either an empty tree, or a binary tree with the following properties. If its left subtree is not empty, the value of all nodes in the left subtree is less than the value of the root structure; If its right subtree is not empty, the value of all nodes on the right alphanter is greater than the value of its root node; Its left and right subtrees are also binary sort trees
Characteristics:
1. Easy sorting
2. Easy to find
3. easy to insert and delete
Question: The Hamming distance between two integers is the number of positions at which the corresponding bits are different. Given two integers x and y, calculate the Hamming distance.
Example:
Input: x = 1, y = 4
Output: 2
Explanation:
1 (0 0 0 1)
4 (0 1 0 0)
↑ ↑
The above arrows point to positions where the corresponding bits are different.
Given the root node of a binary search tree, return the sum of values of all nodes with value between L and R (inclusive). The binary search tree is guaranteed to have unique values.
Example 1:
Input: root = [10,5,15,3,7,null,18], L = 7, R = 15
Output: 32
Example 2:
Input: root = [10,5,15,3,7,13,18,1,null,6], L = 6, R = 10
Output: 23
Heap-Sort is a kind of Selection sort method. It is not Stabled. Mainly used for forming and processing priority queues.
The Principle of the Heap Sort is think the sorting array as the sequential storage structure of a complete binary tree, and the internal relationship between parent nodes and child nodes in the complete binary tree is utilized to select the record with the largest or smallest keyword in the current disordered area.
Time Complexity:
* Average:O(nlog2n)
* Best: O(nlog2n)
* Wirst O(nlog2n)
In a 2 dimensional array grid, each value grid[i][j] represents the height of a building located there. We are allowed to increase the height of any number of buildings, by any amount (the amounts can be different for different buildings). Height 0 is considered to be a building as well.
At the end, the "skyline" when viewed from all four directions of the grid, i.e. top, bottom, left, and right, must be the same as the skyline of the original grid. A city's skyline is the outer contour of the rectangles formed by all the buildings when viewed from a distance. See the following example.
What is the maximum total sum that the height of the buildings can be increased?
Example:
Input: grid = [[3,0,8,4],[2,4,5,7],[9,2,6,3],[0,3,1,0]]
Output: 35
Explanation:
The grid is:
[ [3, 0, 8, 4],
[2, 4, 5, 7],
[9, 2, 6, 3],
[0, 3, 1, 0] ]
The skyline viewed from top or bottom is: [9, 4, 8, 7]
The skyline viewed from left or right is: [8, 7, 9, 3]
The grid after increasing the height of buildings without affecting skylines is:
gridNew = [ [8, 4, 8, 7],
[7, 4, 7, 7],
[9, 4, 8, 7],
[3, 3, 3, 3] ]
Design and implement a data structure for Least Recently Used (LRU) cache. It should support the following operations: get and put.
get(key) - Get the value (will always be positive) of the key if the key exists in the cache, otherwise return -1. put(key, value) - Set or insert the value if the key is not already present. When the cache reached its capacity, it should invalidate the least recently used item before inserting a new item.
The cache is initialized with a positive capacity.
Follow up: Could you do both operations in O(1) time complexity?
Example:
LRUCache cache = new LRUCache( 2 /* capacity */ );
cache.put(1, 1);
cache.put(2, 2);
cache.get(1); // returns 1
cache.put(3, 3); // evicts key 2
cache.get(2); // returns -1 (not found)
cache.put(4, 4); // evicts key 1
cache.get(1); // returns -1 (not found)
cache.get(3); // returns 3
cache.get(4); // returns 4
Given an array nums, write a function to move all 0's to the end of it while maintaining the relative order of the non-zero elements.
Example:
Input: [0,1,0,3,12]
Output: [1,3,12,0,0]
Note:
- You must do this in-place without making a copy of the array.
- Minimize the total number of operations.
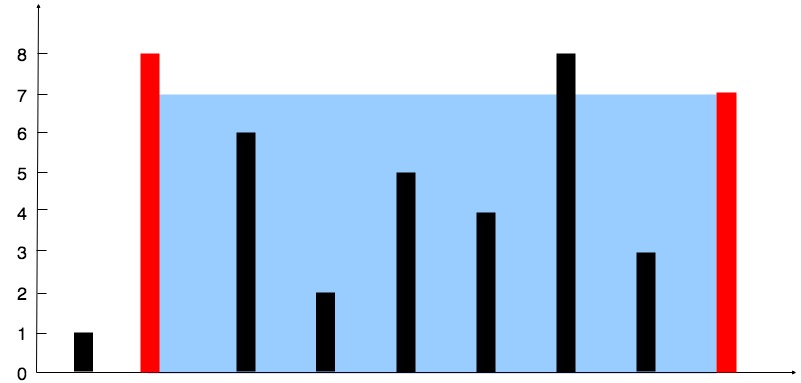
Given n non-negative integers a1, a2, ..., an , where each represents a point at coordinate (i, ai). n vertical lines are drawn such that the two endpoints of line i is at (i, ai) and (i, 0). Find two lines, which together with x-axis forms a container, such that the container contains the most water.
Note: You may not slant the container and n is at least 2.
The above vertical lines are represented by array [1,8,6,2,5,4,8,3,7]. In this case, the max area of water (blue section) the container can contain is 49.
Example:
Input: [1,8,6,2,5,4,8,3,7]
Output: 49
You are climbing a stair case. It takes n steps to reach to the top.
Each time you can either climb 1 or 2 steps. In how many distinct ways can you climb to the top?
Note: Given n will be a positive integer.
Example 1:
Input: 2
Output: 2
Explanation: There are two ways to climb to the top.
1. 1 step + 1 step
2. 2 steps
Example 2:
Input: 3
Output: 3
Explanation: There are three ways to climb to the top.
1. 1 step + 1 step + 1 step
2. 1 step + 2 steps
3. 2 steps + 1 step
Given an array nums of n integers, are there elements a, b, c in nums such that a + b + c = 0? Find all unique triplets in the array which gives the sum of zero.
Note:
The solution set must not contain duplicate triplets.
Example:
Given array nums = [-1, 0, 1, 2, -1, -4],
A solution set is:
[
[-1, 0, 1],
[-1, -1, 2]
]
Given a string containing just the characters '(', ')', '{', '}', '[' and ']', determine if the input string is valid.
An input string is valid if:
Open brackets must be closed by the same type of brackets. Open brackets must be closed in the correct order. Note that an empty string is also considered valid.
Example 1:
Input: "()"
Output: true
Example 2:
Input: "()[]{}"
Output: true
Example 3:
Input: "(]"
Output: false
Example 4:
Input: "([)]"
Output: false
Example 5:
Input: "{[]}"
Output: true
Given n non-negative integers representing the histogram's bar height where the width of each bar is 1, find the area of largest rectangle in the histogram.
Above is a histogram where width of each bar is 1, given height = [2,1,5,6,2,3].
The largest rectangle is shown in the shaded area, which has area = 10 unit.
Example:
Input: [2,1,5,6,2,3] Output: 10
Given an array nums, there is a sliding window of size k which is moving from the very left of the array to the very right. You can only see the k numbers in the window. Each time the sliding window moves right by one position. Return the max sliding window.
Follow up: Could you solve it in linear time?
Example:
Input: nums = [1,3,-1,-3,5,3,6,7], and k = 3
Output: [3,3,5,5,6,7]
Explanation:
Window position Max
--------------- -----
[1 3 -1] -3 5 3 6 7 3
1 [3 -1 -3] 5 3 6 7 3
1 3 [-1 -3 5] 3 6 7 5
1 3 -1 [-3 5 3] 6 7 5
1 3 -1 -3 [5 3 6] 7 6
1 3 -1 -3 5 [3 6 7] 7
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 10^5-10^4 <= nums[i] <= 10^41 <= k <= nums.length